minutes average completion time
An introduction to logistics
In this micro course, we will explore the different functions required to keep modern logistics operations running smoothly – on the ground, in the air, and at sea. We will also look at just a few of the exciting opportunities and careers that exist within logistics.
What is logistics?
Logistics is everywhere. Nearly everything that you touch, eat, open and use has been moved from one place to another. Even if you don’t know what the logistics industry is, you have seen it in action.
Logistics is the process of managing how goods are moved, stored, and transported to their destination.
When we talk about logistics, we are referring to:
- Warehousing and storage.
- Transport and distribution.
Large logistics providers might manage a wide range of operations, from planes and trucks to warehouses and computer software. Smaller logistics providers may be specialists in one or two of these operations.
As wide ranging as the operations that make up logistics, are the types of customers. Manufacturers, retailers, importers, exporters, and home consumers all need logistics to get their goods from point A to point B.

Did you know?
“Logistics” was originally a military term meaning the movement of military personnel, equipment and goods.
The 7 R’s of Logistics
The ‘7 R’s of Logistics’ lays the groundwork for ensuring the smooth operation of all logistics operations.
A common misconception about logistics is that it is all about goods. However, when we explore the ‘7 R’s’, we can see that logistics is really about people.
Many of the ‘R’s’ of logistics are about planning and controlling movement to meet customer needs.
Many different functions are required to keep everything running smoothly. This offers up a wide range of different opportunities and provides many future career possibilities.
During this course, we will explore the key functions involved in logistics and some of the opportunities within them.
Click on the segments below to learn about the different ‘R’s’ of logistics.
Make a note!
Which one of the options below is NOT one of the 7 R’s of logistics?
A. Right place
B. Right time
C. Rapid delivery
D. Right product
Right product
Making sure that the customer receives the right product is essential. Failing to deliver the correct product can lead to negative reviews, returned products and lost customers.
Right quantity
Ordering the right quantity of products delivered is another important rule.
Ordering too many products can lead to excess inventory and storage issues at the warehouse as well as cash flow problems.
Ordering too few products can result in shipping delays, lost business opportunities, and unhappy customers.
Right condition
Making sure goods are in the right condition is the third rule. Goods that are damaged on arrival can damage a company’s reputation, upset customers, and cause delays.
Right place
It is essential that products are delivered to the right place. This is why it is important that logistics companies have a good understanding of the places and countries that they serve.
Right time
Making sure that products arrive at the right time is a priority for all logistics companies.
Customer satisfaction and long-term relationships are impossible to achieve without delivering products on time. Communication is essential to achieve this and many companies now also offer customers tracking information.
Right customer
Customer satisfaction is a priority for every company. For logistics companies, delivering the product to the right customer is essential for achieving this.
Sending the product to the wrong customer is not only embarrassing and costly, but it could lead to severe data breaches.
Right price
By making sure operations run smoothly and avoiding unnecessary costs, logistics companies can offer their services at the right price. This is essential as the right price helps the company to make a profit while keeping customers happy.
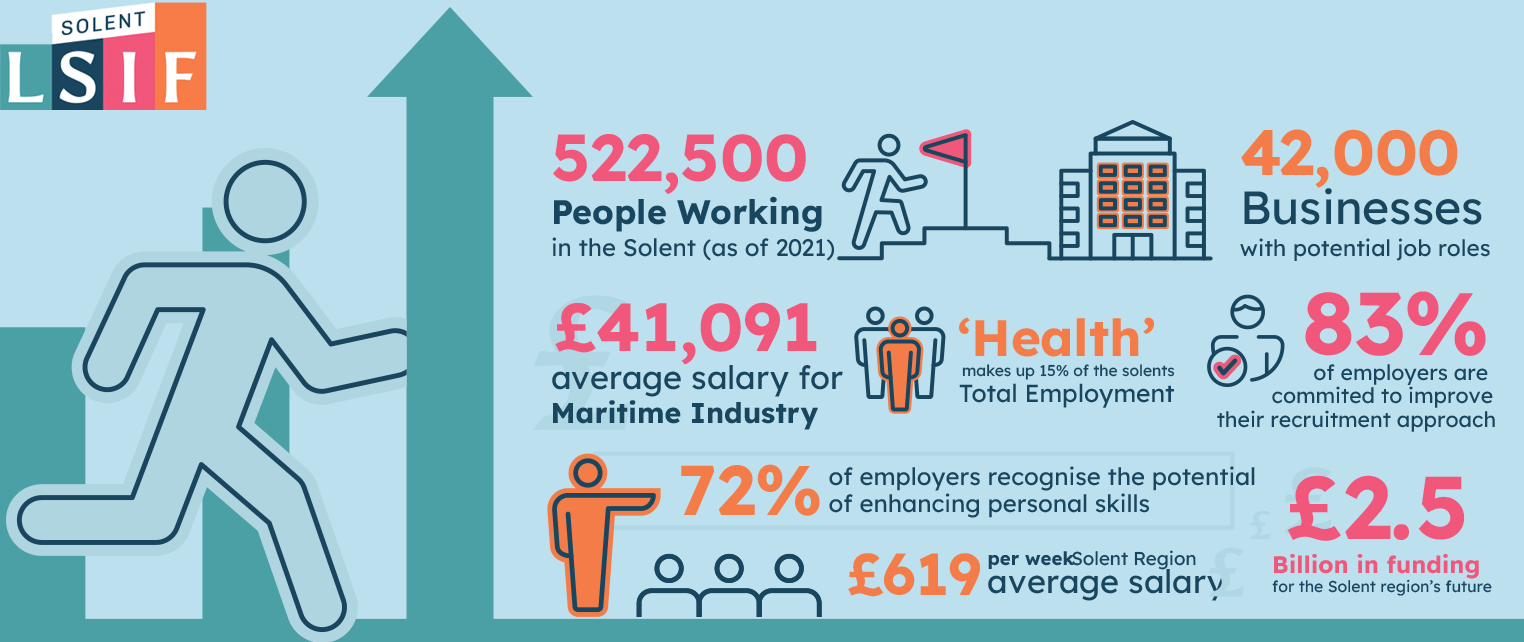
Logistics is Huge!
Career opportunities for you available in the Solent region.
Recent research has highlighted specific career opportunities in the Solent region. This infographic explores key sectors and outlines potential pathways for your future!
What skills would an employer value?
Employers are on the lookout for individuals with a diverse skill set. Possessing these essential skills will greatly improve your chances of securing and excelling in a job.
- Leadership
- Resilience
- Strong Work Ethic
- Digital Literacy
- Creative Thinking
- Professionalism
- Teamwork
- Problem Solving
- Communication
WHICH LEVEL IS RIGHT FOR YOU?
1
Preparing students for Further Education by providing subject-specific content, employability skills, work experience, and the chance to retake English and Maths GCSEs.
2
Helping students enhance core skills before further study. Some technical fields, like Construction and Hairdressing/Beauty, may require starting at Levels 1 or 2 to develop essential hands-on skills.
3
Most common level studied by school leavers who enter Further Education. Typically these courses require 5 GCSE results grade 9-4 including English and Maths or a satisfactory Level 2 grade.
4
Commonly known as Higher National Certificates (HNCs), are designed to support students to develop and expand existing skills from A Level 3 qualification. Level 4 qualifications form the first part of a Foundation Degree, which consists of two years of study.
5
Equivalent to the second year of a Bachelor’s degree and form the second part of a Foundation degree designed to advance the skills and knowledge learnt at Level 4.
6
The primary undergraduate qualification, widely pursued by students. Additionally, you can start with a Foundation Degree and upgrade to obtain a full undergraduate qualification.
Apprenticeships
Apprenticeships offer a work-based path to qualifications from Level 2 and up, with smooth transitions and multiple supported routes.
Students can move from a full-time Level 2 or 3 programs to Apprenticeships, or advance to university from a Level 3 Apprenticeship. In certain fields, Apprenticeships are preferred, fostering academic skills alongside workplace experience.
THE BIGGEST OPPORTUNTIES FOR YOU IN THE SOLENT
Maritime & Logistics
Her Role is Just One of the
10,000 Jobs
expected in this industry
Lots of Roles to choose from, with
20,000 FTE Jobs
Vocational / Technical study to Postgraduate Levels in
Maritime Business, Operations
Secure Your Future Role in
Ports, Leisure Marine, Marine Engineering, Port Logistics

Take the next step towards your future
There are fantastic opportunities waiting for you in these sectors and beyond in the Solent region!
Did you know?
Engaging in programs with the highlighted partners in this document will aid you in enhancing your proficiency in these skills, while also equipping you with the necessary abilities for success in your chosen field.
Warehousing & Storage
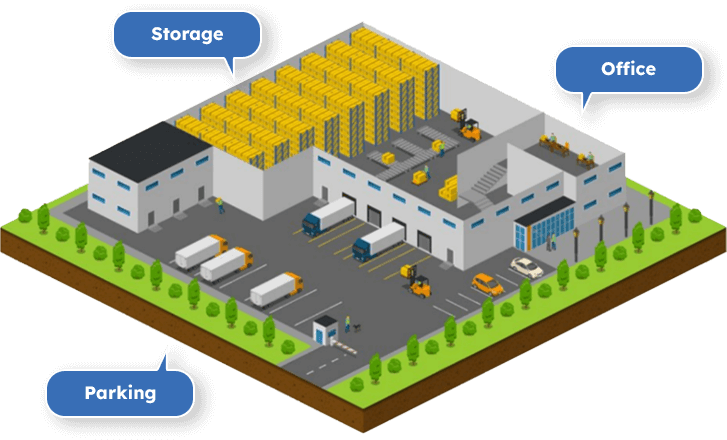
A warehouse is a building used for storing goods.
They serve a wide range of customers including manufacturers, importers, exporters, wholesalers and customs.
The image below shows a simple warehouse overview.

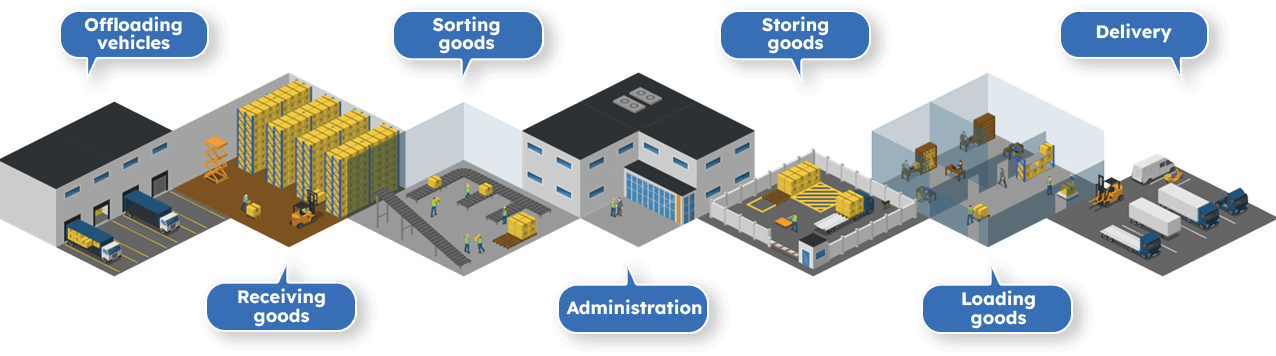
Warehouses must be able to store many different types of goods. Because of this, there are different types of warehouses, and each type of warehouse fulfils a specific need.
Different warehouses
Click on the buttons below to learn about the roles of different warehouses…
The growth in eCommerce and increasing demands from consumers has seen a significant change in warehouse operations.
Technology has revolutionised the way warehouses operate. Many of the repetitive tasks involved in warehousing can now
be automated.
Automated vehicles can load and unload goods from vehicles and then stack them on to the shelves. Machines can also perform automated picking.
Many warehouses also use powerful software called a warehouse management system (WMS) that helps to organise and streamline all their operations.
This increased use of technology not only helps to improve existing jobs, but it also creates new ones. This has made the industry attractive for people who want to work with innovative technologies, such as robots and artificial intelligence (AI).

Example careers in Warehouses
Click on the buttons below to learn about some of the different roles in warehouses…
Private Warehouse
Private warehouses are owned and operated by companies such as manufacturers and wholesalers.
They are used to distribute goods across the company’s supply chain.
They can form part of a large network.
Public Warehouse
Public warehouses are commercial spaces that provide storage facilities for a charge.
They are commonly used by smaller traders.
Large companies may also use them to store extra stock.
Automated Warehouse
In automated warehouses, computers and robotics are used to store and retrieve goods.
The ‘automation’ ranges from simple conveyor belt to robotic arms that pick and move goods.
They are highly efficient, fast, and agile facilities.
Climate-controlled Warehouse
Climate-controlled warehouses are specialised facilities that maintain a constant temperature and humidity.
They hold temperature-sensitive products, such as refrigerated foods, pharmaceuticals, and vaccines.
Distribution Warehouse
Distribution centres are used for goods near the end of the supply chain (goods ready for distribution).
Goods are usually stored for a short time, sometimes just a matter of hours!
Bonded Warehouse
Bonded warehouses are used to store imported goods.
Goods are stored until a customs duty (a type of taxation) is paid on them.
Bonded warehouses are commonly located near ports, where imported goods arrive.
Make a note!
What does the acronym WMS stand for?
Warehouse operative
Other names: Warehouse worker, warehouse picker
Average Salary: £16,000-£24,000 a year (or £1,333 – £2,000 per month)
Warehouse operatives take delivery of goods and pack orders for dispatch.
In this role you could:
- Take in deliveries and check for damaged or missing items.
- Use lifting equipment to move stock around the warehouse.
- Check stock levels and make sure items are stored correctly.
- Pack, wrap and load items to be dispatched.
- Clean the warehouse.
Forklift driver
Other names: Forklift operator, forklift truck driver
Average Salary: £17,000-£30,000 (or £1,416 – £2,500 per month)
Forklift drivers load and unload goods in warehouses, ports, and airports.
In this role you could:
- Check equipment daily and use it safely.
- Load and unload goods from lorries, ships or aircraft.
- Use radio frequency equipment to keep in touch with other staff.
- Manually handle goods when necessary.
- Stack goods and move them around in storage bays.
- Pick and pack orders.
- Complete paperwork for delivery notes and stock control.
Database administrator
Database administrators create, organise, and look after computer systems that store data for a company.
Average Salary: £24,000-£45,000 (or £2,000 – £3,750 per month)
As a database administrator, you would:
- Fill the database with new information or transfer existing data into it.
- Plan how to update information, create back-up copies, and report errors.
- Identify other systems the database will link to.
- Plan how to organise, find, and display data.
Storage
Businesses often store their inventory in warehouses. Warehouses decide on the best way to store inventory to make it easily accessible and to prevent theft or damage.
Office
As well as storing goods, warehouses need space for the different roles needed to keep things running smoothly.
Warehouses will often have staff dealing with administration, finance, technology, and learning and development.
Parking
Warehouses need to have dedicated spaces for lorries and vans as well as parking for employees, visitors and customers.
Offloading vehicles
Most goods that arrive at a warehouse will be offloaded in preparation for storage.
The exception to this rule is known an ‘cross-docking’. Cross docking is when cargo is unloaded from one vehicle and then immediately loaded directly on to an outbound vehicle to continue its journey.
Receiving goods
When receiving goods, a warehouse will confirm that it has received the correct product, in the correct amount, in the correct condition, and at the correct time.
Warehouse staff can use software to create barcodes that can track goods as they move through the warehouse.
Sorting goods
Once goods have been received, the process known as ‘put-away’ can begin. Put away refers to various tasks that happen between receiving goods and having them all put away into their assigned places.
One of these tasks is to identify where the received goods can be kept safely in the correct conditions and arrange for them to be taken there.
Administration
Warehouse administrators oversee the management of stock and often use warehouse management system and other technologies.
This forms the backbone of efficient warehouse operations. A warehouse must keep track of how many items they have stored so they know when it’s time to restock.
Storing goods
Storing goods is the operation of placing things in the most suitable storage area. Goods must be stored in the right direction, optimum temperature, and right height.
Vehicles and technologies may also support with this, such as fork-lift trucks, robots, and automated machinery.
Loading goods
Goods must be protected during transit so that they are delivered to customers in perfect condition. Care is taken to load and store goods correctly and make sure they are secured properly.
Delivery
The product is ready to see its new home! Some warehouses have their own vehicles but most have an agreement with courier services who operate the vehicles.
Methods of Transportation: Road
Road freight is fast and reliable and has the unique benefit of offering door-to-door delivery.
Road freight is essential for many businesses and the demand for road freight is expected to triple by 2050.
The food industry could not survive without road freight. Approximately 98% of food and agriculture products are transported by road.
Even if goods are partly transported in by air, sea, or rail, they must be transported those last few miles by road. This is known as ‘the last mile’.
An important issue in road freight is the European Green Deal. This is a set of policies with an aim to decrease carbon dioxide emissions (CO₂) by 90% by 2050.
In response to this, transport companies are optimising their routes and in the longer term will be increasing their use of electric vehicles.

The European Green Deal is a set of policies with an aim to decrease carbon dioxide emissions (CO₂) by 90% by 2050.

Example careers in Road Transport
Click on the buttons below to learn about some of the different roles in road freight…
Did you know?
Although the name implies that it refers to the final mile of delivery, the range of ‘last mile’ can span from under one mile to 100 miles!
Make a note!
What do me mean by ‘last mile logistics’?
Import-export clerk
Other names: Shipping agent, freight forwarder, import-export agent
Average Salary: £18,000-£30,000 (or £1,500 – £2,500 per month)
Import-export clerks ship goods to and from the UK by road, rail, air, and sea.
In your day-to-day duties you could:
- Manage freight bookings using a computer system.
- Check that tax and customs documents are correct.
- Work with national and international suppliers and agents.
- Arrange freight deliveries and collections between ports, airports, and warehouses.
- Handle invoices and payments.
- Keep clients up to date and deal with problems or delays.
Heavy goods vehicle driver
Other names: LGV driver, lorry driver
Average Salary: £22,000-£40,000 (or £1,8333 – £3,333 per month)
HGV drivers transport and deliver products between suppliers and customers.
As a HGV driver, you could:
- Plan deliveries and the route you’ll take.
- Check your vehicle is safe and report any issues you find.
- Help load and unload goods safely.
- Keep records of the deliveries you make.
- Regularly check traffic reports and change your route if needed.
Transport & distribution clerk
Transport and distribution clerks perform various clerical functions relating to the transport and distribution of goods and freight.
Average Salary: £18,000-£35,000 (or £1,500 – £2,916 per month)
In this role you could:
- Maintain records regarding the movement and location of freight, containers and staff.
- Obtain customs clearance and processes import and export documentation necessary for the movement of goods between countries.
- Monitors tachograph readings and maintains records of hours worked and distance travelled by drivers.
- Formulates delivery loads, vehicle schedules and routes to be followed by delivery staff.
- Processes customer orders and forwards requisition documentation to storage and distribution personnel.
Methods of Transportation: Air Freight
Air freight is very reliable and is usually the fastest transport option available
This means that time-sensitive goods are often transported by air. Air freight also benefits from being highly protected from theft or damage, making it ideal for high-value goods.
Air freight is essential in keeping the UK competitive in world business and many industries, such as pharmaceuticals, technology, and food, depend on it.
Air freight operations are carried out by thousands of people, all with specific jobs to keep things running smoothly.
Air freight operations are made possible by the operations of UK airports and ground handling services, which employ over 400,000 people.
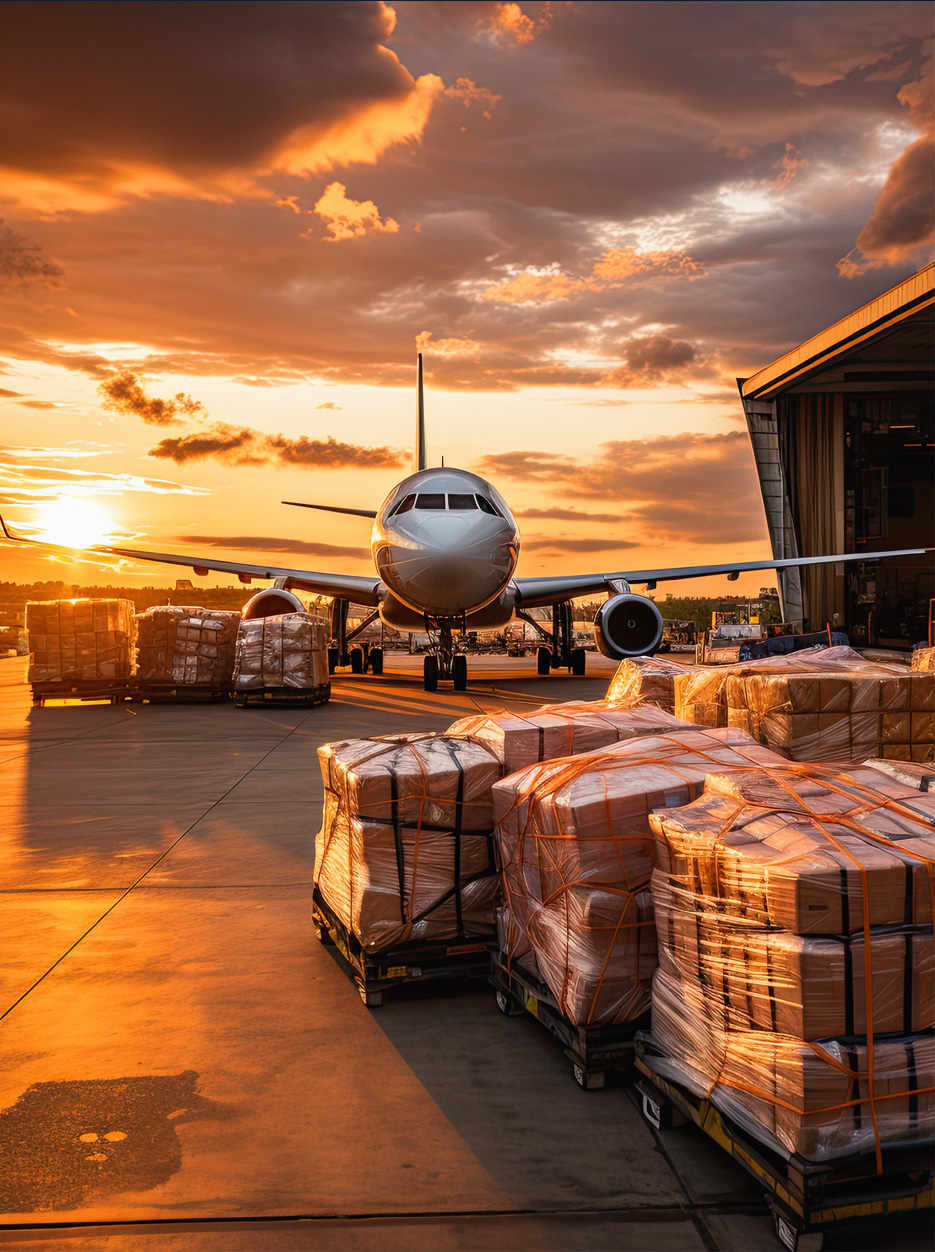

Airports are essential for the movement of high value or urgent goods in and out of the UK.

Example careers in Air Freight
Click on the buttons below to learn about some of the different roles in air freight…
Did you know?
Without air freight, the concept of ‘express delivery’ wouldn’t exist. Air freight has reduced the length of time shipments take from weeks or months to a matter a hours in some cases!
Make a note!
What type of goods are especially suited to air freight?
Customer service assistant
Other names: Customer service adviser
Average Salary: £17,000-£25,000 (or £1,416 – £2,083 per month)
Customer service assistants deal with customer questions, purchases, and complaints.
In this role you could:
- Answer customer questions by phone, email, webchat, social media or in person.
- Give quotations and check product availability.
- Sell products or services and take payments.
- Handle complaints or pass them to a supervisor.
- Add customer information onto a computer.
- Track orders and arrange deliveries.
Ground handling agent
Average Salary: £20,000-£28,000 (or £1,666 – £2,333 per month)
Ground handling agents ensure the efficient and effective arrival, turnaround, and departure of aircraft.
You could work on an aircraft, at an airport or in a warehouse.
In this role you could:
- Move cargo to and from aircraft holds using trucks, cargo loaders and conveyor systems.
- Store cargo in warehouses.
- Help aircraft prepare for flight.
Import-export clerk
Other names: Shipping agent, freight forwarder, import-export agent
Average Salary: £18,000-£30,000 (or £1,500 – £2,500 per month)
Import-export clerks ship goods to and from the UK by road, rail, air, and sea.
In your day-to-day duties you could:
- Manage freight bookings using a computer system.
- Check that tax and customs documents are correct.
- Work with national and international suppliers and agents.
- Arrange freight deliveries and collections between ports, airports and warehouses.
- Handle invoices and payments.
- Keep clients up to date and deal with problems or delays.
Methods of Transportation: Water Freight
The shipping industry in the UK is made up of ports, harbours, shipping lines, and the inland waterway network.
Water freight offers one of the cheapest transport options and has the added benefit of being the most environmentally friendly option. Freight moved by water produces less carbon dioxide (CO₂) than road, rail, and air.
When we talk about water freight, we are referring to:
- Ocean freight.
- Inland waterway freight.
Ocean Freight
As the UK is an island, shipping has played a very important role in history and remains an essential part of everyday life.
Ocean freight is essential for moving ‘bulk cargo’. Bulk cargo refers to goods that are moved unpackaged in large quantities. Bulk cargo is classified as ‘liquid’ or ‘dry’ and includes oil, iron ore (used to create steel), and grain. These shipments would not be possible by road, rail, or air.
Another important aspect of shipping is container shipping. Containers allow for the fast unloading and offloading of cargo, and their invention also gave birth to the concept of intermodal transportation.
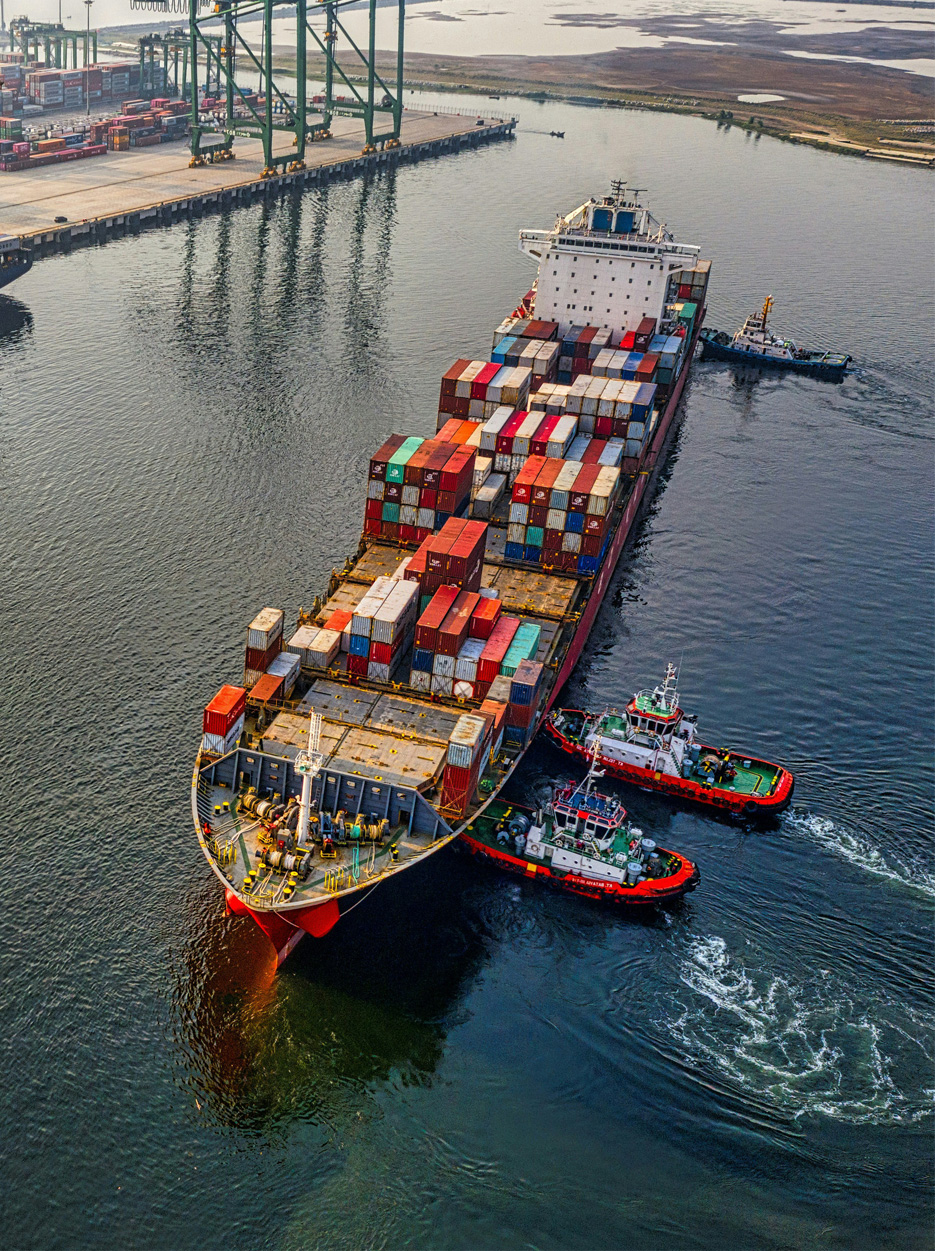

Ocean freight operations are made possible by the UK port industry. The UK port industry is the second largest in Europe and handles approximately 500 million tonnes of freight each year.
UK ports employ over 100,000 people and play a crucial role in the country’s economy. Approximately 95% of the UK’s international trade is carried through UK ports.
The UK’s ten largest ports handle more than 300m tonnes of freight each year.
Inland Waterways
The UK’s inland waterways include many marine areas that is not a sea or ocean. This includes canals, lochs, rivers, and estuaries.
A key benefit of using inland waterways to move goods are the positive environmental and economic impacts. Moving goods by inland waterway helps to reduce road congestion and emissions – and can also provide work for more rural communities.
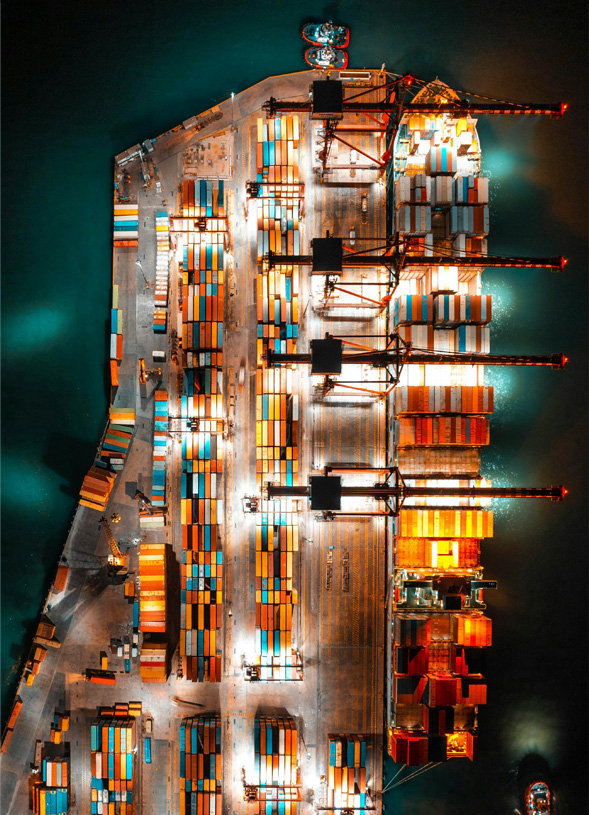


Example careers in Water Freight
Click on the buttons below to learn about some of the different roles in water freight…
Did you know?
Before shipping containers were invented, it could take up to 3 weeks to load and unload ships. This can now be completed in as short a time as one day.
Did you know?
One benefit of inland waterways is that they can support abnormally large loads. Airbus used the River Dee to transport airplane wings during the development of the Airbus A380.
Make a note!
What do we mean by bulk cargo?
Marine engineering technician
Average Salary: £24,000-£43,000 (or £2,000 – £3,583 per month)
Marine engineering technicians design, build, service and repair boats and ships.
As a marine engineering technician, you could:
- Diagnose faults and repair equipment on a ship.
- Refurbish older ships with new navigation and communications systems.
Port operative
Other names: Stevedore, port worker, passenger operations worker
Average Salary: £16,000 to £27,000 (or £1,333 – £2,250 per month)
Port operatives work with cargo and marine craft in ports and harbours.
As a port operative you could:
- Load and unload cargo containers, using ship or dockside cranes.
- Transfer cargoes to storage areas with trailers or forklift trucks.
- Operate conveyors and pumps for bulk cargoes like grain, coal, and oil.
Import-export clerk
Other names: Shipping agent, freight forwarder, import-export agent
Average Salary: £18,000-£30,000 (or £1,500 – £2,500 per month)
Import-export clerks ship goods to and from the UK by road, rail, air, and sea.
In your day-to-day duties you could:
- Manage freight bookings using a computer system.
- Check that tax and customs documents are correct.
- Work with national and international suppliers and agents.
- Arrange freight deliveries and collections between ports, airports and warehouses.
- Handle invoices and payments.
- Keep clients up to date and deal with problems or delays.
Methods of Transportation: Rail
Rail freight’s importance to the UK goes back to the early 19th century and it has played a crucial role in transporting coal, mail, and military equipment.
Rail freight continues to be important today and contributes nearly £2.5 billion to the UK economy every year. Rail freight use is steadily increasing, and it is expected to play an even larger role in the movement of goods in the UK over the next 10 years.
Growth in rail freight is important because of the environmental benefits it can bring, such as helping to reduce congestion on the road.
Commonly transported goods by rail include coal, oil, construction materials, and cars.
‘Liner train’ and ‘freightliner’ are terms for trains that carry intermodal containers. There are major intermodal freight terminals throughout England in rail terminals, seaports, and airports.
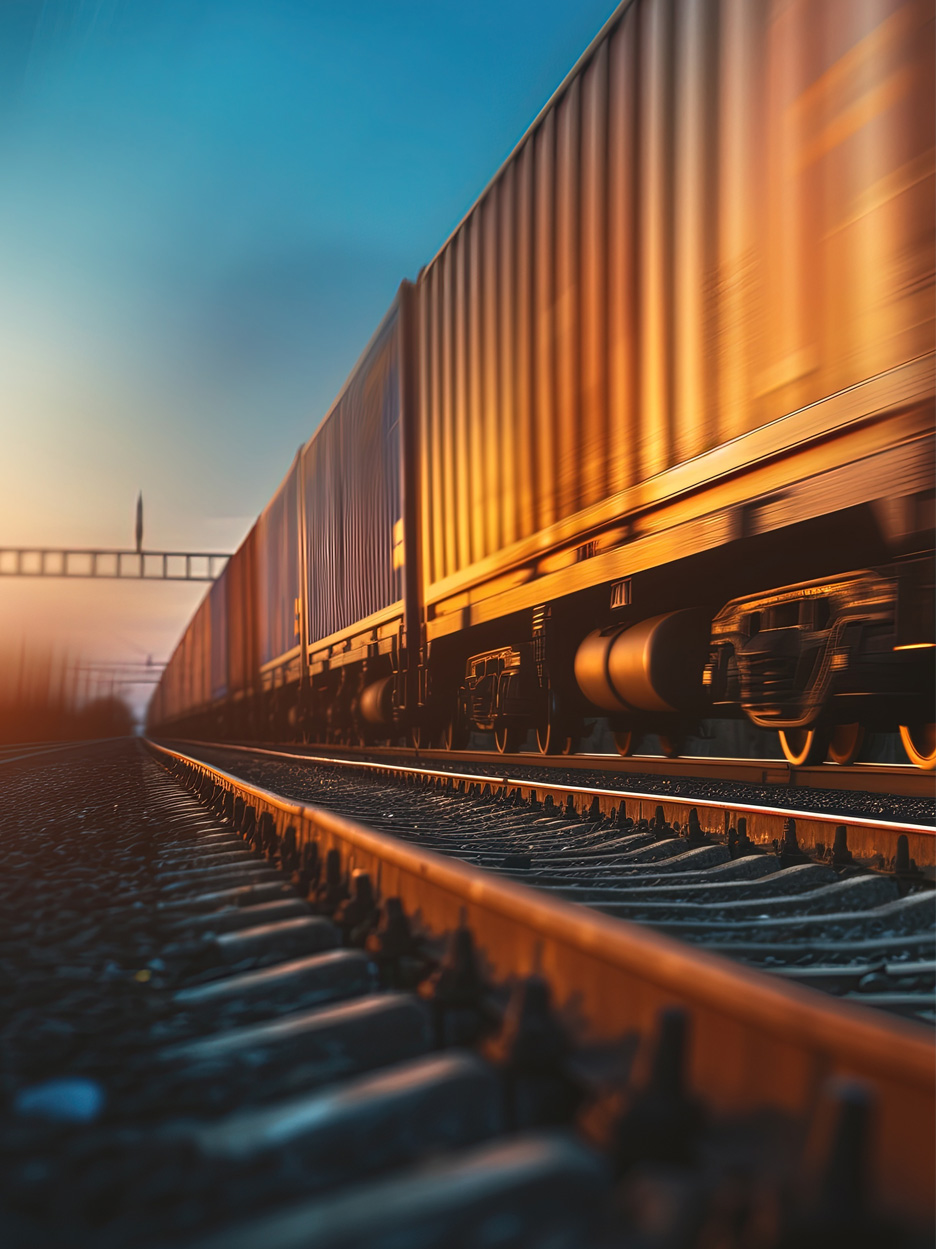

The rail network in Great Britain has been used to transport goods since the early 19th century.

Example careers in Rail
Click on the buttons below to learn about some of the different roles in rail…
Did you know?
A single rail freight movement can remove over 100 Large Goods Vehicle (LGV) movements on the road.
Make a note!
What is the benefit of intermodal containers?
Train driver
Average Salary: £24,000-£65,000 (or £2,000 – £5,416 per month)
Train drivers operate trains on the rail network, carrying passengers and freight around the country.
In this role you’ll:
- Check controls and equipment before a journey.
- Drive the train between stations or freight depots.
- Speak with control centres along the route about any issues.
- Follow track signalling, safety, and speed instructions.
- Leave platforms and pull into stations safely.
- Make passenger announcements.
- Control automatic doors.
- Position and hand over engines to drivers on the next shift.
- Record incidents like equipment problems, onboard issues, or delays.
Rail engineering technician
Average Salary: £30,000-£45,000 (or £2,500 – £3,750 per month)
Rail engineering technicians service, maintain and repair train engines, carriages and other rail vehicles.
In this role you’ll:
- Follow written technical instructions.
- Install lighting, control panels and communication systems in engines and carriages.
- Inspect bodywork and undercarriages for defects or damage.
- Repair or replace parts.
- Make regular checks on brakes and couplings.
- Take apart, test and reassemble mechanical, electrical and pneumatic systems.
- Write service reports and update maintenance records.
Finance officer
Other names: Financial officer, finance clerk, treasurer
Average Salary: £19,500-£34,000 (or £1,625 – £2,833 per month)
Finance officers help to manage the finances of an organisation by keeping track of its income and controlling its spending.
As part of your day-to-day duties, you could:
- Record financial transactions on computer systems.
- Produce financial forecasts.
- Deal with payroll, invoices, expenses, and VAT.
- Resolve payment questions for external contractors.
- Carry out financial audits.
- Create budget reports.
- Present reports to managers.
Career Path Questionnaire
This simple questionnaire might help you to identify some career pathways that suit your personal interests and your skills. This questionnaire comes in 2 parts. The first part of this activity is a simple questionnaire.
Using the options in the table below, answer each of the questions by selecting a number in one of the columns, based on the following:
1 = Dislike a lot 2 = Dislike 3 = Don’t Mind 4 = Like 5 = Like a lot
Based on your personal interest and skills, you may be interested in the jobs shown in the highlighted section below.
Working with IT and projects
Roles explored in this course:
- Marine engineering technician
- Rail engineering technician
You may also enjoy other careers in engineering, information technology, and energy.
You scored
in this category.
Working with people and processes
Roles explored in this course:
- Transport and distribution clerk
- Database administrator
- Import-export clerk
- Customer service assistant
- Finance officer
You may also enjoy other careers in learning and development, human resources, and customer service.
You scored
in this category.
Working on your feet or outdoors
Roles explored in this course:
- Warehouse operative
- Heavy goods vehicle driver
- Forklift driver
- Ground handling agent
- Port operative
You may also enjoy other careers in manufacturing warehousing, airports, and sea ports.
You scored
in this category.
8 Steps to Get You Started
- Make a list of your personal strengths and interests
- Follow logistics companies on social media
- Check out the careers section in the library
- Speak with a career’s advisor
- Explore apprenticeship options in transport and logistics
- Look at the skills required for careers that interest you
- Create a portfolio of your favourite achievements
- Set and follow-up on career-related goals



Check Your Knowledge
So now you’re well on the way to understanding about Logistics, answer the multi-choice questions below to see how much you really know.
Good luck!
Well done. You have successfully achieved the pass mark for this course. All the correct answers are now shown.
You haven’t achieved the pass mark on this occasion. Have another go.
You haven’t quite reached the pass mark for this course, but all of the correct answers are now shown. Please study these before moving on, or feel free to go back and look again at any of the pages of this course.