
minutes average completion time
Import – Export
In this micro course, we will explore how goods and services are traded between different countries. We will also look at just a few of the exciting opportunities and careers that support the importing and exporting of goods.
International Trade & the UK
International trade is the purchase and sale of goods and services by companies in different countries.
International trade in the UK began in the 17th Century between India and the UK, global trade has been a key part of the UK economy since.
Today, globalisation has opened many new markets and created opportunities for businesses to expand their reach further than ever before. The UK is currently the 6th largest country in terms of international trade.
Importing refers to the process of purchasing goods or services from overseas and bringing them into the UK. Most companies import some products and services.
Some items are imported because they cannot be manufactured in the UK due to the climate.
Items may also be imported because it is cheaper to purchase products from another country than to make them in the UK.
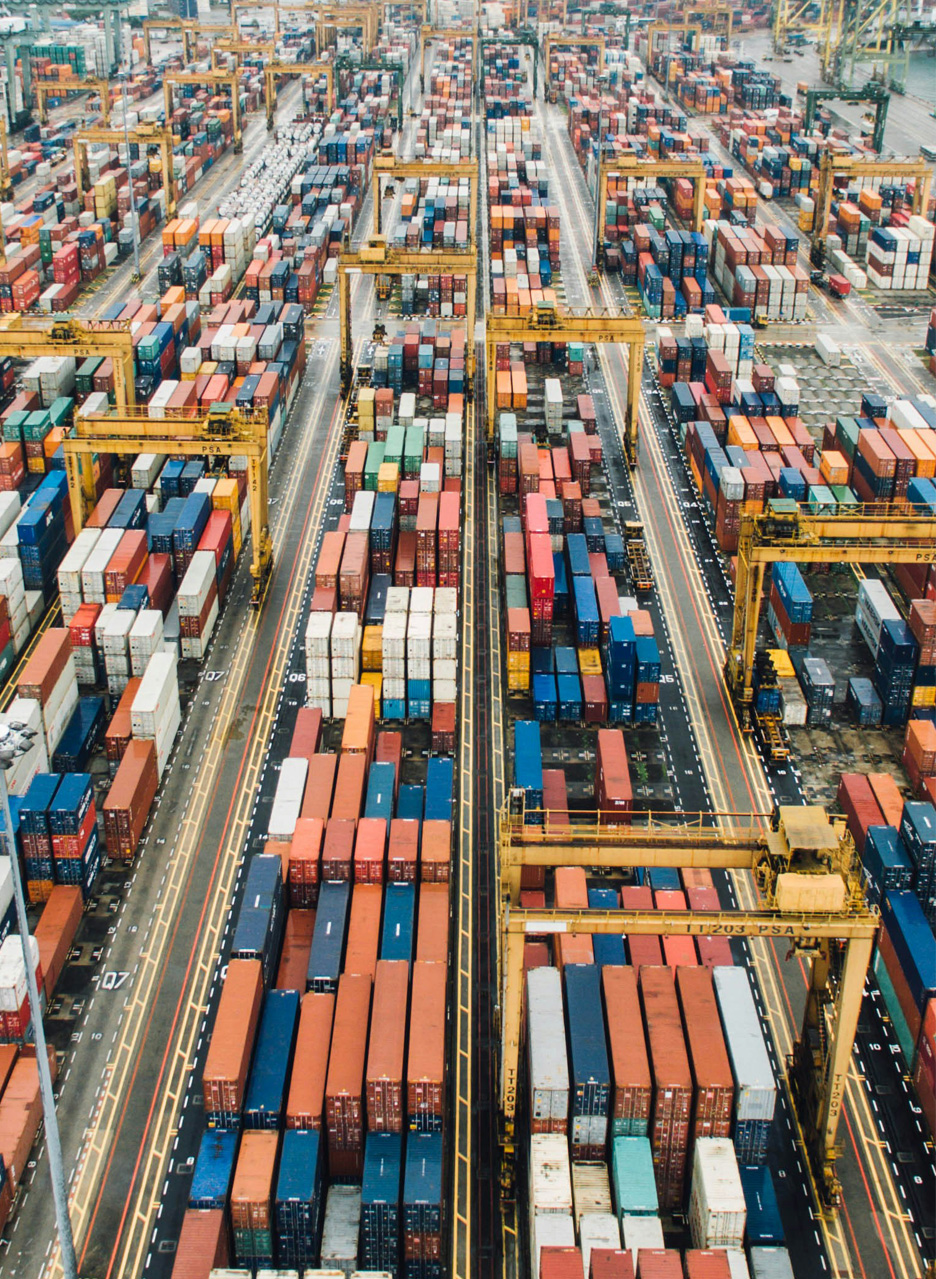

Exporting refers to the UK selling products and services to other countries around the world. Exporting goods and services brings money into the UK economy.
One of the UK’s biggest exports are vehicles. Other important UK exports include pharmaceuticals, power generators, and crude oil.
Brexit was the withdrawal of the United Kingdom from the European Union (EU). Before that, the UK was part of the EU.
Prior to Brexit there were no customs borders between EU states. This virtually eliminated the customs delays and documentation required to move goods between the UK and Europe. Following Brexit, many UK companies are now considered international importers and exporters.
International trade is a complex and interesting topic, with many laws, regulations, and constant updates. In this book, we will explore some of the key areas of international trade and some of the career opportunities it brings.

Import-export: Customs
‘Customs’ refers to an organisation that is responsible for controlling the flow of goods in and out of a country.
An essential task when importing or exporting goods is to make a customs declaration.
Goods moving in and out of the UK need customs clearance to make sure they are not restricted or prohibited. Goods also need to be checked to make sure whoever is receiving them pays the right amount of tax and duty.
Customs is a complex and interesting topic, with many laws, regulations, and constant updates. Because of this, skills and experience in the topic are highly sought after by employers.
Many businesses will use a specialist company to make customs declarations for them.
Border Force are part of the UK Home Office. They are responsible for undertaking immigration and customs controls at the UK borders.
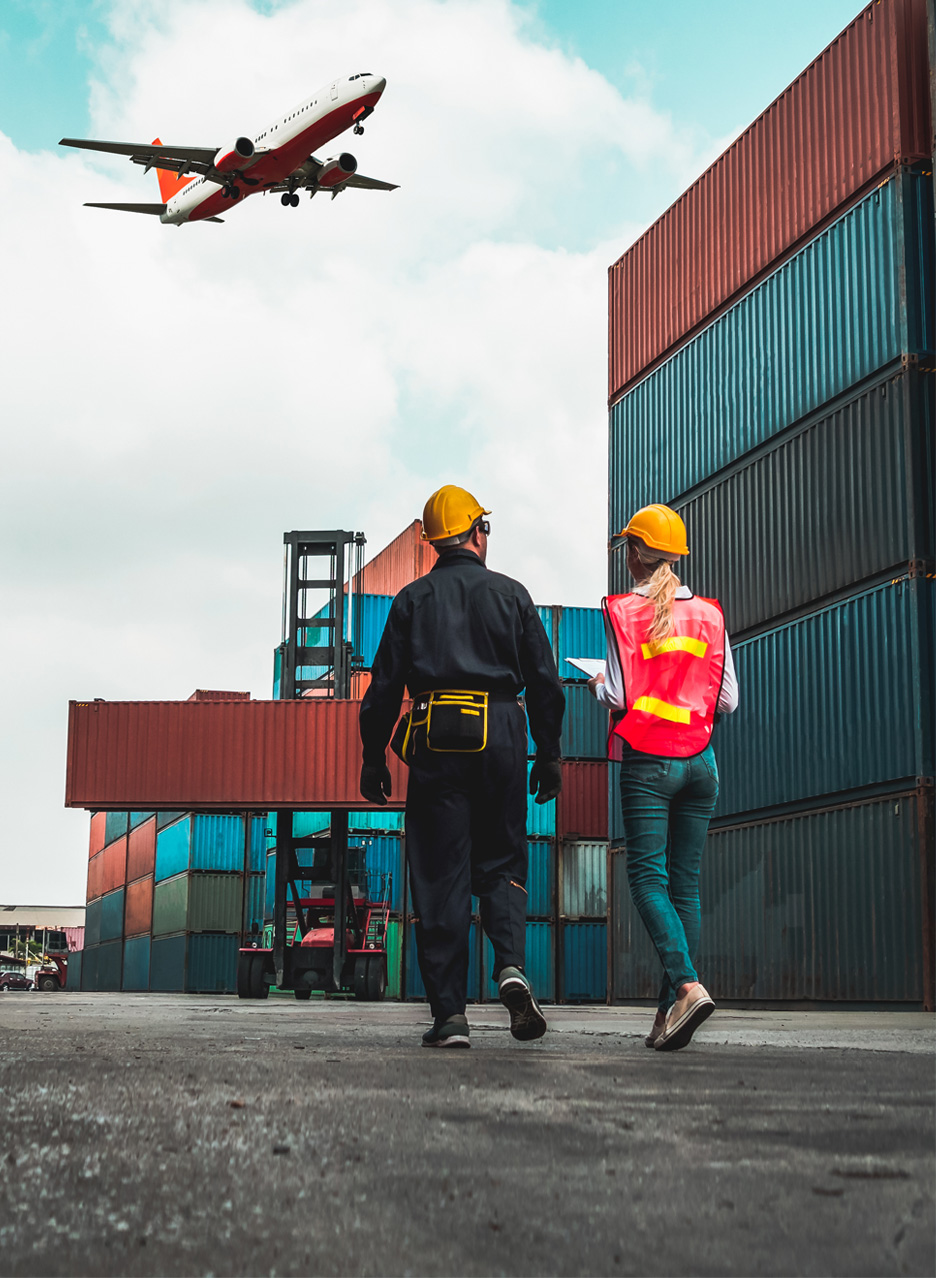

Border Force covers 140 seaports and airports and one of their priorities is to protect customs revenues.

Did you know?
International Customs Day is celebrated in January every year.
Make a note!
Who is responsible for undertaking immigration and customs controls at the UK borders?
Import-export: Taxes & Duties
Taxes have been an important part of life for centuries. A tax is a deduction from something you get or own, or an additional cost added to something you buy. It is not a fine for doing something wrong.
Normally, governments collect taxes so that there is a pot of money to spend for the benefit of society. Taxes help to pay for:
- Health and social care services.
- Welfare services.
- Schools and universities.
- Transport systems.
- Policing.
- Other vital areas.
Value-added tax (or VAT) is a purchase tax added onto items that are bought (except things deemed ‘essential’, such as food). VAT is a percentage of the item’s cost which is determined by the government. Currently, VAT stands at 20%.
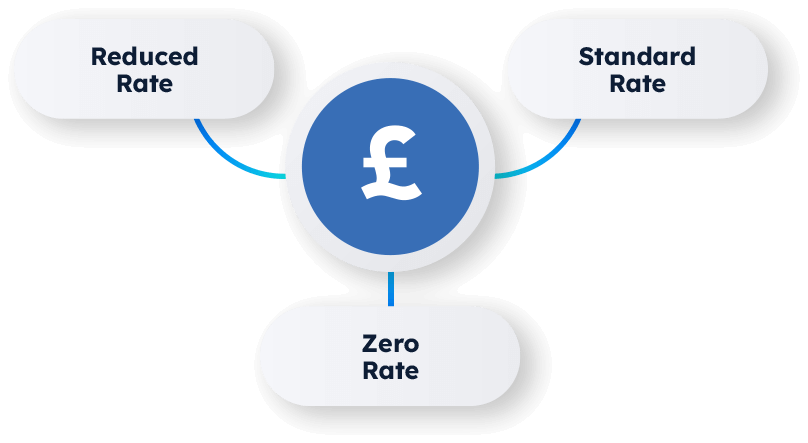
There are 3 different rates of VAT:

Customs duties are taxes imposed on the import and export of goods. The rates of customs duties vary according to the goods involved and international agreements between the relevant countries.
Did you know?
VAT has been around for over 50 years and is one of the 3 largest sources of government revenue, along with income tax and national insurance.
Make a note!
What is the current standard rate of VAT?
Standard rate
Most goods and services are standard rate, which is currently 20%.
Reduced rate
A reduced rate of 5% applies to some goods and services.
This includes health products, fuel, heating, and car seats for children.
Zero rate
Zero-rated means that the rate of VAT charged to customers is 0%.
Children’s clothes and most types of food are zero-rated.
Import-export: Trade Agreements & Trade Sanctions
Trade agreements set out the rules for buying and selling goods and services between 2 or more countries. They can reduce restrictions on imports and exports, which makes trading easier and cheaper.
Global trade agreements started coming into existence in the late 20th century and today there are more than 100 trade agreements. Nearly every country in the world is involved in at least one trade agreement.
Rules of origin show where goods originate from. They also identify which goods are covered in trade agreements.
All internationally traded goods are required to have an origin when they are declared to customs at the point of import and at the time of export.
In contrast to trade agreements the UK government can also impose trade sanctions with certain countries. A trade sanction is a trade penalty against a country in response to negative behaviours or actions.

Examples of incidents that can lead to trade sanctions include:
- Violations of international law.
- Violations of human rights.
- Armed conflict.
- International terrorism.
The Department for International Trade is responsible for implementing trade sanctions in the UK. A serious breach of sanctions is generally a criminal offence, with large fines payable and the possibility of prison sentences for individuals.

Make a note!
What is the purpose of ‘rules of origin’?
Import-export: Trade Controls
Trade controls are restrictions placed on the transfer of certain items from one country to another.
Trade controls are not unique to the UK, nearly every country in the world has some form of trade control. Trade controls typically apply to military-related goods, but there are still many everyday goods that require an import license or export license.
Import and export licences are required for goods that the Government wants to be carefully monitored when they enter or leave UK borders.
Import Licenses
A food import license is required if the imported food falls into the ‘high risk’ category.
This refers to goods which could potentially cause harm if they don’t meet food safety standards. Examples of goods requiring a food import license include those containing salmonella or pesticides.

Other types of goods that require an import license include:
- Plants or plant products.
- Animals or animal products.
- Medicines.
- Weapons.
Export Licenses
UK exports are controlled for various reasons, but they are typically concerned with preventing harm to others as well as protecting the national security of the UK and its allies. Most export controls relate to military goods. However, trade controls can also relate to ‘dual use’ items.
Dual-use items are goods that can be used for both civil and military applications. This includes certain types of drones, chemicals, and some computer software.

Make a note!
True or False: An import license is required to import food into the UK?
Import-export: Dangerous Goods
Dangerous goods are items that may endanger the safety of people, equipment and the environment.
Mistakes when moving dangerous goods can be disastrous. Explosions, fires, toxic exposures, and environmental contamination are just some of the hazards associated with the mishandling of hazardous goods.
Transporting dangerous goods is covered by national and international laws and each type of transport must follow its own set of rules to ensure that dangerous goods are moved safely.
Dangerous goods are split into 9 classes according to the type of danger that they present.

If a substance is found to meet the classification criteria for any of the 9 classes of dangerous goods, the transport of the goods must comply with the dangerous goods regulations for the type of transport used.

Did you know?
All perfumes and colognes that contain alcohol are considered a ‘dangerous good’.
Make a note!
How many classes of dangerous goods are there?
Class 1: Explosives
Commonly shipped examples include:
- Fireworks
- Flares
- Blasting caps
- Fuses
- Explosive charges
Class 2: Gases
Commonly shipped examples include:
- Aerosols
- Compressed air
- Fire extinguishers
- Insecticide gases
- Refrigerant gases
Class 3: Flammable Liquids
Commonly shipped examples include:
- Acetone
- Adhesives
- Alcohols
- Perfumery products
- Fuel
Class 4: Flammable Solids
Commonly shipped examples include:
- Alkali metals
- Sodium batteries
- Firelighters
- Matches
Class 5: Oxidisers
Commonly shipped examples include:
- Chemical oxygen generators
- Ammonium nitrate
- Chlorates
- Nitrate
- Nitrites
Class 6: Toxic & Infectious Substances
Commonly shipped examples include:
- Medical/Biomedical waste
- Clinical waste
- Biological samples/specimens
- Medical samples/specimens
- Tear gas substances
Class 7: Radioactive Material
Commonly shipped examples include:
- Radioactive ores
- Medical isotopes
- Density gauges
Class 8: Corrosives
Commonly shipped examples include:
- Acids
- Batteries
- Battery fluid
- Paint
- Dyes
- Fire extinguisher charges
Class 9: Miscellaneous
Commonly shipped examples include:
- Dry ice
- Battery-powered equipment
- Chemical kits
- First aid kits
- Air bag modules
- Seatbelt pretensioners
Import-export: Careers in Import-export
Example careers
Click on the images below to learn about some of the different roles in Import and Export…

Import-export clerk
Import-export clerks ship goods to and from the UK by road, rail, air and sea.
Average Salary: £18,000-£30,000 (or £1,500 – £2,500 per month)
In this role you could:
- Manage freight bookings using a computer system.
- Check that tax and customs documents are correct.
- Work with national and international suppliers and agents.
- Arrange freight deliveries and collections between ports, airports and warehouses.
- Handle invoices and payments.
- Keep clients up to date and deal with problems or delays.
Border Force Officer
Border Force officers protect UK border entry points like ports and airports, by enforcing immigration and customs regulations.
Average Salary: £26,000-£32,000 (or £2,166- £2,666 per month)
In this role you could:
- Check travel documents and passports.
- Question passengers about their reasons for visiting the UK.
- Search people, luggage, and vehicles.
- Work with the police and immigration officials on operations.
- Write case notes and reports.
- Attend court as a witness.
Career Path Questionnaire
This simple questionnaire might help you to identify some career pathways that suit your personal interests and your skills. This questionnaire comes in 2 parts. The first part of this activity is a simple questionnaire.
Using the options in the table below, answer each of the questions by selecting a number in one of the columns, based on the following:
1 = Dislike a lot 2 = Dislike 3 = Don’t Mind 4 = Like 5 = Like a lot
Based on your personal interest and skills, you may be interested in the jobs shown in the highlighted section below.
Working with IT and projects
Roles explored in this course:
- Marine engineering technician
- Rail engineering technician
You may also enjoy other careers in engineering, information technology, and energy.
You scored
in this category.
Working with people and processes
Roles explored in this course:
- Transport and distribution clerk
- Database administrator
- Import-export clerk
- Customer service assistant
- Finance officer
You may also enjoy other careers in learning and development, human resources, and customer service.
You scored
in this category.
Working on your feet or outdoors
Roles explored in this course:
- Warehouse operative
- Heavy goods vehicle driver
- Forklift driver
- Ground handling agent
- Port operative
You may also enjoy other careers in manufacturing warehousing, airports, and sea ports.
You scored
in this category.
8 Steps to Get You Started
- Make a list of your personal strengths and interests
- Follow logistics companies on social media
- Check out the careers section in the library
- Speak with a career’s advisor
- Explore apprenticeship options in transport and logistics
- Look at the skills required for careers that interest you
- Create a portfolio of your favourite achievements
- Set and follow-up on career-related goals



Check Your Knowledge
So now you have an understanding about Import-export, it’s time to
answer the multi-choice questions below to see how much you really know.
Good luck!
Well done. You have successfully achieved the pass mark for this course. All the correct answers are now shown.
You haven’t achieved the pass mark on this occasion. Have another go.
You haven’t quite reached the pass mark for this course, but all of the correct answers are now shown. Please study these before moving on, or feel free to go back and look again at any of the pages of this course.

